The Critical Role of Scope 2 Emissions in Data Center Sustainability Efforts
Published on February 13, 2024,
by
As the digital era intensifies, the demand for data storage and processing capabilities skyrockets, inadvertently leading to a surge in data center electricity usage. With a recent IEA report1 indicating that data center electricity consumption is poised to double by 2026, the spotlight is increasingly on the environmental impact of these digital behemoths. Central to this concern is Scope 2 emissions, which, although indirect, constitute a significant portion of a data center's carbon footprint due to their substantial electricity needs.
Scope 2 emissions stem from the energy that data centers purchase to power their operations. These emissions are not generated onsite but are released into the atmosphere by the utility providers that supply electricity to the facilities. Since data centers are among the most significant corporate consumers of electricity, their influence on Scope 2 emissions is profound. Understanding and mitigating Scope 2 emissions becomes paramount as these facilities strive for sustainable operations.
The alarming projection1 that data center electricity use could exceed 1,000TWh by 2026, primarily due to power-hungry applications like AI and cryptocurrency mining, underscores the urgency of addressing these emissions. Notably, the 460TWh consumed by data centers in 2022 accounted for a staggering two percent of global electricity usage, spotlighting the significant environmental impact of these operations.
In response to this growing concern and climate legislation3, innovative solutions like Nlyte Software's Data Center Sustainability Compliance Reporting Solution are emerging to aid data center operators in their sustainability endeavors. This tool allows operators to track their total carbon dioxide equivalent (TCO2e) emissions and many other critical sustainability metrics, providing a clear picture of their environmental impact. Furthermore, the solution's Renewable Energy Factor (REF) metric enables data centers to measure how much they offset their carbon footprint using renewable energy sources. For instance, a data center responsible for 100 kt(CO2e) but with a REF of 0.25 effectively reduces its net emissions to 75 kt(CO2e), showcasing a tangible step towards sustainability.
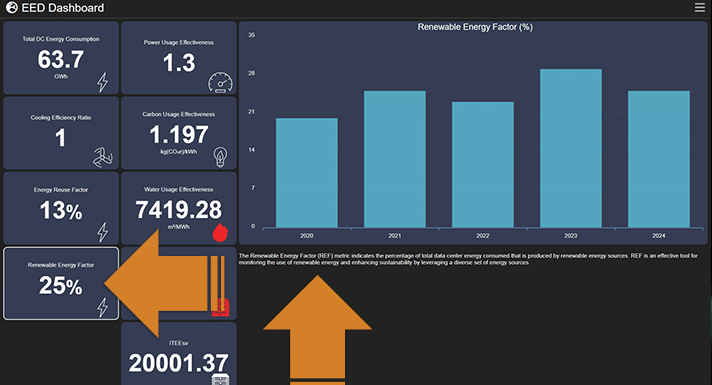
Renewable Energy Factor (REF) as displayed in the Nlyte Software Data Center Sustainability Dashboard for the EU EED compliance reporting.
However, the journey towards reducing Scope 2 emissions doesn't stop at merely tracking and offsetting carbon output. Data center operators must also explore innovative technologies and strategies to enhance energy efficiency and increase the use of renewable energy sources. Solutions like Nlyte Energy Optimizer are crucial in this endeavor, enabling operators to optimize their energy consumption and further diminish their environmental impact.
The path to sustainability is multifaceted, involving advanced technology, strategic planning, and a commitment to renewable energy. As data centers expand to meet the insatiable demand for digital services, their role in global sustainability efforts becomes increasingly significant. By prioritizing the reduction of Scope 2 emissions and embracing renewable energy, data center operators can lead the charge toward a more sustainable digital infrastructure, ensuring that the growth of the digital realm does not come at the expense of our planet's health.
References and Additional Resources
1 Electricity 2024 - Analysis and forecast to 2026 (windows.net)
2 Global data center electricity use to double by 2026 - IEA report - DCD (datacenterdynamics.com)
Reducing Data Centers' Carbon Footprint: Strategies and Tools for Sustainability
What is PUE and how is it Calculated?
White Paper: Fundamental Measures of Data Center Sustainability
Executive Brief: Climate Risk Disclosures in Data Centers - A Review of the Proposed SEC Guidelines
Executive Brief: Singapore's Data Centre Energy Efficiency Scheme (DCS)

